Reply to the Comments on “Case Series: Successful resuscitation of Severe facial Injuries Caused by a Chainsaw”
Article information
I would like to sincerely thank you for your interest in my previous study, and to answer the questions that you asked in your comments published in JTI [1].
For case 1, I can present several radiographs comparing between preoperative and postoperative status of the bony structures of the mandible (Fig. 1). There are no pictures of the mouth gag being applied to the patient.
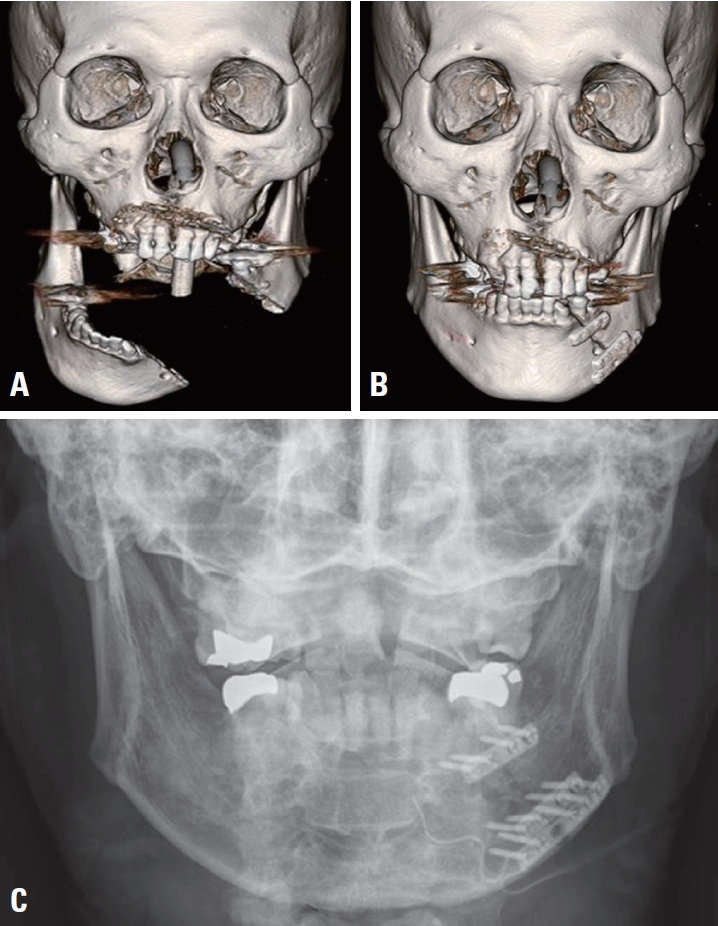
Three-dimensional reconstructed computed tomography images of the patient in case 1, (A) before and (B) af ter the reconstructive operation. (C) A simple X-ray series of the mandible shows successful end-to-end restoration of the bony structures.
In case 2, fortunately, there was no evidence of lacrimal canalicular injury before and after the operation. The patient described in case 2 recovered well, without neurological complications.
As mentioned in my previous paper, there are no accurate data about the incidence and injury patterns of chainsaw-related injuries in South Korea. In Europe (including Serbia), the most common site of injuries caused by chainsaw-related accidents was found to be the head (34.8%). On the contrary, the hands and knees were reported to be the most frequent sites in the United States [2,3]. With the goal of providing optimal care, I agree with your suggestion that early involvement of a plastic surgeon is essential.