Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Trauma Inj > Volume 35(4); 2022 > Article
-
Original Article
Outcomes after rib fractures: more complex than a single number -
Kristin P. Colling, MD1,2
 , Tyler Goettl, MD1
, Tyler Goettl, MD1 , Melissa L. Harry, PhD3
, Melissa L. Harry, PhD3
-
Journal of Trauma and Injury 2022;35(4):268-276.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.20408/jti.2021.0096
Published online: August 5, 2022
- 2,451 Views
- 74 Download
1Department of Surgery, University of Minnesota Medical Center, Minneapolis, MN, USA
2Department of Trauma Surgery, Essentia Health-St. Mary's Medical Center, Duluth, MN, USA
3Essentia Institute of Rural Health, Duluth, MN, USA
- Correspondence to Kristin P. Colling, MD Department of Trauma, Essentia Health-St. Mary’s Medical Center, 10 West, 407 East 3rd Street, Duluth, MN 55805, USA Tel: +1-218-786-4210 E-mail: kristin.colling@essentiahealth.org
Copyright © 2022 The Korean Society of Traumatology
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
-
Purpose
- Rib fractures are common injuries that can lead to morbidity and mortality.
-
Methods
- Data on all patients with rib fractures admitted to a single trauma center between January 1, 2008 and December 31, 2018 were reviewed.
-
Results
- A total of 1,671 admissions for rib fracture were examined. Patients’ median age was 57 years, the median Injury Severity Score (ISS) was 14, and the median number of fractured ribs was three. The in-hospital mortality rate was 4%. Age, the number of rib fractures, and Charlson Comorbidity Index scores were poor predictors of mortality, while the ISS was a slightly better predictor, with area under the receiver operating characteristic curve values of 0.60, 0.55, 0.58, and 0.74, respectively. Multivariate regression showed that age, ISS, and Charlson Comorbidity Index score, but not the number of rib fractures, were associated with significantly elevated adjusted odds ratios for mortality (1.03, 1.14, and 1.28, respectively).
-
Conclusions
- Age, ISS, and comorbidities were independently associated with the risk of mortality; however, they were not accurate predictors of death. The factors associated with rib fracture mortality are complex and cannot be explained by a single variable. Interventions to improve outcomes must be multifaceted.
- Rib fractures are common injuries, occurring in 10% to 15% of all trauma patients [1,2]. Rib fractures are often associated with polytrauma and may occur alongside head, abdominal, chest wall, pulmonary, or spinal injuries, which can complicate the management of these patients [1–4]. Research suggests that older patients are at significantly higher risk of mortality and morbidity associated with rib fractures [5–7], although the age at which the risk increases is still unclear. Researchers have suggested that injuries experienced by those older than 65 years [6,8], 55 years [9], and 45 years [10] can be defined as “elderly rib fractures.” As aging research continues, it is becoming clear that age is, in fact, “only a number,” and that the overall health status, degree of frailty, and number of comorbidities of patients present at the time of their rib fractures may better explain poor outcomes than patient age. Therefore, treatment for rib fractures must be tailored to each patient. Treatment guidelines are often based on a simplification of risk factors, especially based on age, and overall adherence to guidelines tends to be poor [11]. In a study of geriatric patients with multiple rib fractures, Shi et al. [12] found that, among those who had not been directly admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU), 9% had an unplanned admission; however, they did not observe an associated difference in outcomes in patients who experienced unplanned ICU admission.
- Patients over 65 years of age with rib fractures, patients with three or more rib fractures, and patients with polytrauma are recommended to be transferred to a trauma center for care. However, data on the outcomes of transfer patients are lacking. Our trauma center, Essentia Health-St. Mary's Medical Center (Duluth, MN, USA), serves a large, rural area, and a sizable proportion of our patient population is transferred to us for treatment. The goals of this study were threefold: (1) to describe the population of patients admitted to our trauma center with rib fractures; (2) to compare demographic and injury-related characteristics as well as the outcomes of patients who were directly admitted to our center and patients who were transferred to our center; and (3) to identify possible risk factors for increased mortality.
INTRODUCTION
- Ethical statements
- This study was reviewed, approved, and monitored throughout by the Institutional Review Board of Essentia Institute of Rural Health. Due to the retrospective nature of the study, informed consent was waived.
- Patient selection
- We performed a retrospective observational study of all trauma patients admitted from January 1, 2008 to December 31, 2018 to Essentia Health-St. Mary’s Medical Center (SMMC-EH), a single trauma center, located in northeastern Minnesota, which serves a large area of rural communities. SMMC-EH was a level II American College of Surgeons (ACS) verified adult and pediatric trauma center throughout the majority of the study period and was reclassified as a level I ACS adult trauma center in September 2018. Since SMMC-EH is a large referral center serving an expansive area spanning three states, many patients are transferred to our hospital after an initial evaluation at a local hospital. Most hospitals that refer patients to SMMC-EH are located in rural areas, based on Rural-Urban Commuting Area codes [13], and many are critical access hospitals (CAHs) [14]. We included all patients admitted after a traumatic injury with at least one rib fracture during the study period who met the National Trauma Data Standard patient inclusion criteria [15]. The only exclusion criteria were patients who elected not to participate in research at our institution.
- Data collection
- All patient data were electronically extracted from the SMMC-EH trauma registry and electronic health records. Patient demographics included age at admission, sex, race, ethnicity, Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) score, alcohol use, tobacco use, and the number of unique rib fracture hospitalizations during the study period. Hospitalization-related variables included the mechanism of injury, number of ribs fractured, Injury Severity Score (ISS), ICU admission (and whether it was planned upon initial examination or unplanned), length of ICU stay, mechanical ventilator use and duration of use, rib fixation, noninvasive ventilation use (bilevel positive airway pressure or continuous positive airway pressure), and the use of epidural or catheter-based anesthesia for pain control. Outcome variables included the length of hospital stay, in-hospital complications (e.g., pneumonia or sepsis), discharge disposition, 30-day inpatient readmissions, 30-day emergency department admissions, and mortality. Patient transfer status was determined for all hospitalizations (i.e., if patients were admitted directly after presenting at the SMMC-EH emergency department or were admitted after being transferred from another hospital). For patients who were transferred to our facility, the ACS’s trauma designation (level II, III, or IV, or undesignated) and whether they were designated by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services as a CAH were collected from all transferring hospitals. The CAH designation is designed to support rural hospitals, reduce financial strain, and improve access to care by enabling access to healthcare services in rural areas. To meet CAH definitions, hospitals must (1) have 25 or fewer inpatient beds, (2) be more than 35 miles from other hospitals, (3) have an average length of stay of fewer than 96 hours for inpatients, and (4) provide emergency care services 24 hours a day and 7 days a week [14]. The duration of time spent at the local hospital (defined as the time of admission to the local hospital to discharge from the local hospital) and the transfer time (the time from discharge from the local hospital to the time of admission at the trauma center) were calculated for all patients transferred to our hospital. During the final years of the study period (August 2017 to August 2018), our standard clinical practice was to assess all patients admitted to our center who were aged 65 years and older using the Edmonton Frailty Scale [16]. This scale was administered by trauma team staff through patient or caretaker interviews, and the data were recorded in the patients’ charts. The scores were then abstracted via a chart review. Frailty data were only available for a subset of patients since, prior to August 2017, these data were not collected.
- Data analysis
- Our primary outcome measures were in-hospital complications, median length of stay in the hospital, discharge disposition, and mortality (in the hospital, within 30 days, and within 1 year). All analyses were performed in IBM SPSS ver. 23.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). We reported the demographics of patients as medians and ranges for all continuous variables, since they were not normally distributed, or as the number of patients and percentages. Descriptive statistics were used to examine the study population. Demographic comparisons between directly admitted and transfer patients were made using the chi-square test (or the Fisher exact test when cell counts were <5) and the Mann-Whitney U-test. Since some patients had more than one hospitalization for a rib fracture during the study period, some analyses were performed using the first admission only. When all admissions were analyzed, bivariate and multivariate generalized estimating equations were employed when comparing outcomes between transferred and directly admitted patients, since patients could have been included in one of the groups multiple times for separate admissions. generalized estimating equations included negative binomial and binary logit-linked models with unstructured correlation matrices. Binary logistic regression was also used to make comparisons between unique patients. In these analyses and tables, we clearly outlined when only the first rib fracture admission and when all rib fracture admissions were included. A P-value of less than 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance.
METHODS
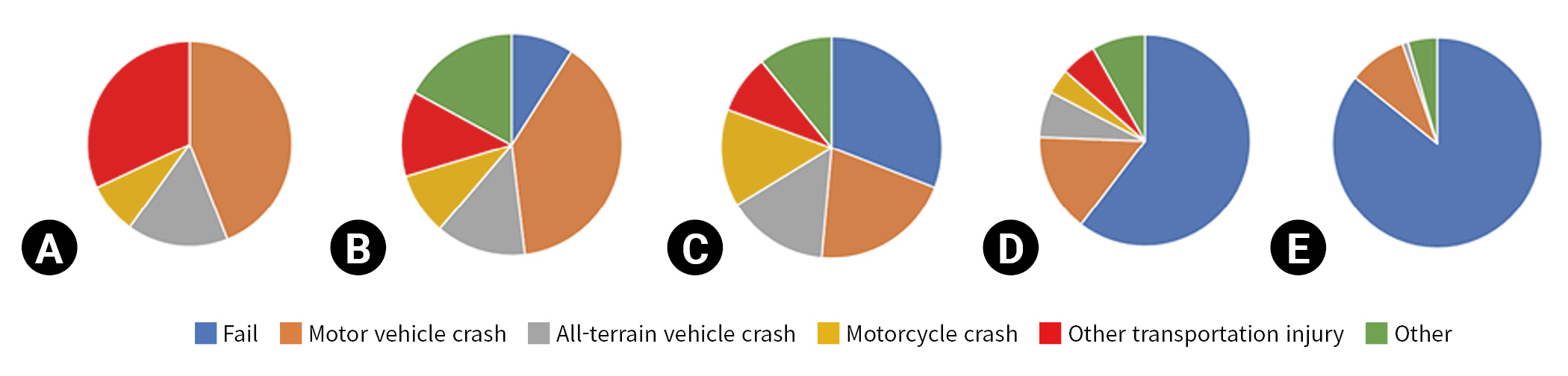
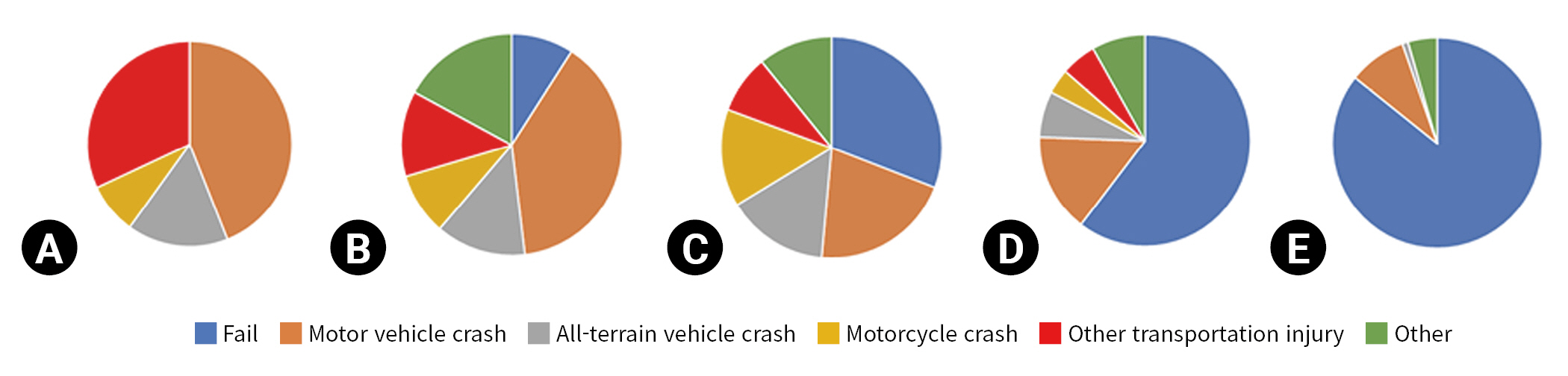
- During the study period, 1,649 patients were admitted for rib fractures, with 1,671 unique rib fracture hospital admissions. The majority of patients were Caucasian (92.6%), followed by American Indian/Alaska Native (4.9%) and Black (0.5%). Patients were more likely to be male than female (male patients, 71.2%; female patients, 28.8%). Patients experienced between one and three unique rib fracture hospital admissions during the study period. The median age at hospitalization was 57 years (range, 2–98 years), and the median ISS was 14 (interquartile range [IQR], 9–18). The median number of rib fractures was 3 (IQR, 2–5). Among the total hospitalizations, 592 hospitalizations (36%) related to rib fractures required an ICU stay, with 10% requiring transfer to the ICU after floor admission. The most common mechanism of injury was falling, followed by motor vehicle, all-terrain vehicle, and motorcycle crashes; however, the mechanism of injury varied greatly based on the age group (Fig. 1). In the pediatric age group, vehicle-related injuries (whether motor vehicle, all-terrain vehicle, motorcycle, or other) accounted for 100% of rib fractures. As age increased, the number of injuries caused by falls also increased. Alcohol use was common, with 26% of admissions being associated with alcohol use on the day of injury. Active tobacco use was also high at 27.8%.
- Transfer status
- During the study period, 894 patients (54%), representing 902 hospital admissions, were transferred to our trauma center from other hospitals for definitive care. Most patients were initially evaluated as having been transferred from an ACS level IV trauma center (67%), followed by undesignated trauma centers (20%) and level III centers (13%). Eighty-two percent of patients were transferred from CAHs. The median time spent at the initial hospital was 2.71 hours (IQR, 1.60–4.07 hours), and the median transportation time from the initial hospital to the trauma center was 1.18 hours (IQR, 0.68–1.57 hours). Compared to direct admission, transfer patients were more often male and more often sustained their injuries due to high-impact mechanisms such as motor vehicle or all-terrain vehicle crashes. As shown in Table 1, transfer patients tended to be younger, more likely to actively use tobacco, and sustain injuries associated with alcohol use than directly admitted patients. Transfer patients were less likely to have a CCI score of 2 or more (10.5% for transfer patients vs. 19.5% for directly admitted patients). The median ISS was higher for transfer patients. The median number of rib fractures was similar between groups. Approximately one-third of all patients in both groups were admitted to the ICU; however, transfer patients were significantly more likely to experience unplanned ICU admission (12% for transfer patients vs. 9% for directly admitted patients; P=0.041). The rate of pneumonia did not differ between the groups.
- In-hospital mortality
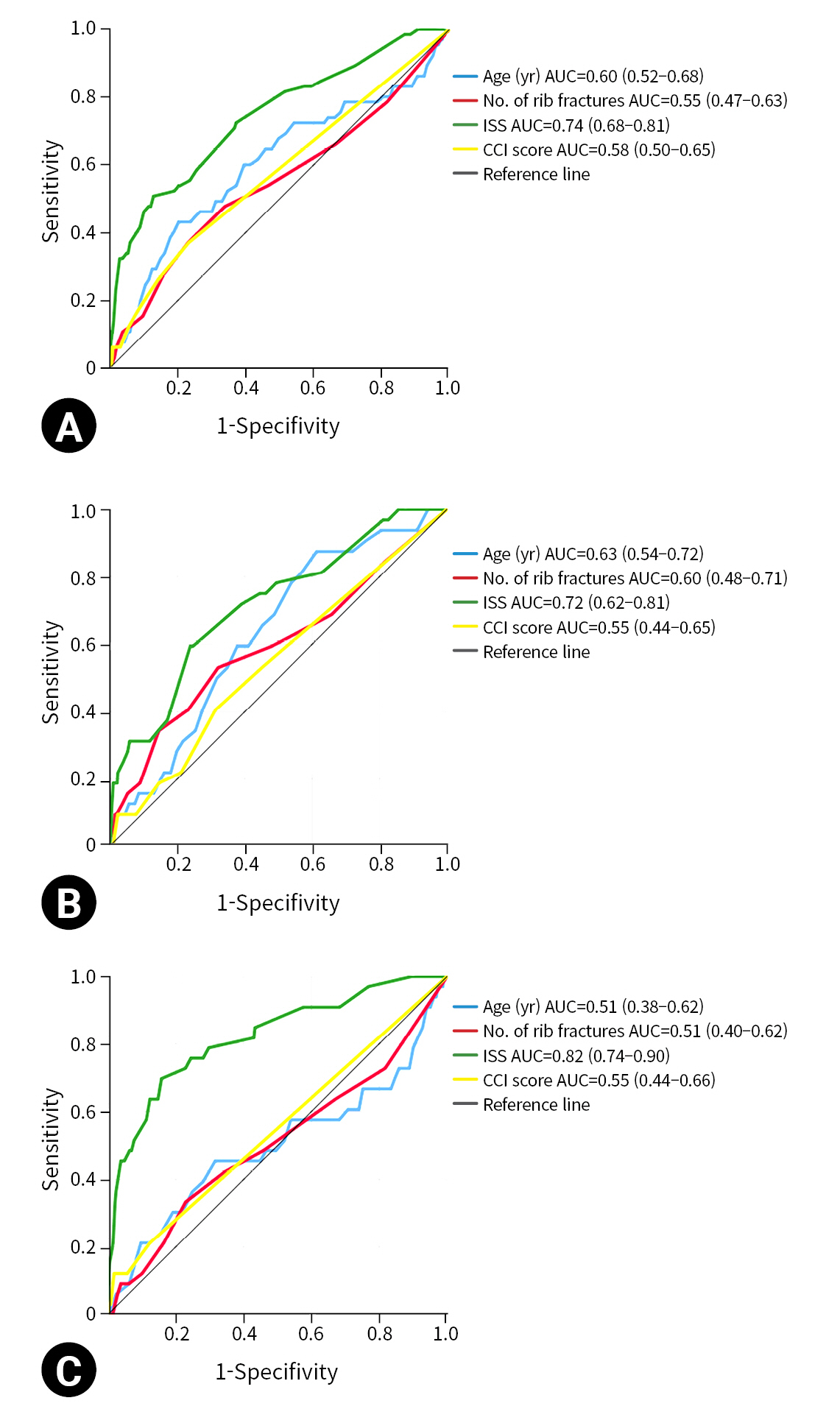
- All in-hospital mortality analyses were performed using the information on each unique patient information for their first rib fractures as opposed to data on all hospitalizations. The total number of unique patients was 1,649. One patient died during their second admission and was not included in this mortality analysis. In-hospital mortality was 4.1% and did not significantly differ between directly admitted patients (4.2%) and transfer patients (3.9%). Patients who required ICU admission had a higher in-hospital mortality rate compared to those who did not require ICU admission (7.3% and 2.2%, respectively; P<0.001), but there was no significant difference between patients with planned and unplanned ICU admissions (7.1% vs. 7.6%; P=0.92). Patients who died in hospital (median age, 64 years; IQR, 47–80 years) tended to be significantly older than survivors (median age, 56 years; IQR, 43–69 years; P=0.013). However, age was not an effective predictor of mortality, and in a receiver operating characteristic curve, the area under the curve was only 0.60 (95% confidence interval, 0.52–0.68) (Fig. 2A). Similar to age, the number of rib fractures and the CCI score were poor predictors of mortality using receiver operating characteristic curves (Fig. 2A). ISS was a better predictor of in-hospital mortality. Table 2 depicts the odds ratios and adjusted odds ratios of in-hospital mortality for age, number of rib fractures, CCI score, and ISS calculated using univariate analysis and binary logistic regression.
- Patients aged 65 years and older with rib fractures
- In a subgroup analysis, we evaluated 565 hospitalizations of 553 patients aged 65 years and older, which included a comparison to those younger than 65 years of age (Table 3). Falls were overwhelmingly the most common cause of injury within the older group of patients; however, transfer patients were more likely to be admitted for injuries caused by other mechanisms (Table 3). Transfer patients had a significantly higher median ISS and were more likely to be admitted to the ICU upon admission. However, even with a higher median ISS and likelihood of ICU admission, no significant differences in in-hospital or 30-day postdischarge mortality were observed between transfer patients and directly admitted patients.
- Compared to younger patients, patients older than 65 years of age did not have a significantly increased risk of in-hospital mortality (aged ≥65 years, 5.8%; aged <65 years, 4.1%; P=0.13). Patients younger than 65 years of age were more likely to require ICU admission than older patients (38.6% vs. 30.6%, respectively; P=0.001) and were more likely to have an unplanned ICU admission (12% vs. 6.7%; P<0.001). Receiver operating characteristic curves predicting mortality were created using age, ISS, number of rib fractures, and the CCI score for those aged 65 years and older and those under 65 years of age, and they are depicted in Figs. 2B and 2C. In both groups, age was a poor predictor of mortality. ISS was a more specific and sensitive predictor of mortality in younger patients. The number of rib fractures and comorbidities were poor predictors of mortality in both groups, but they were slightly better predictors in the older age group.
- Frailty
- Frailty in 76 patients aged 65 years and older was assessed using the Edmonton Frail Scale [16]. In this subgroup, 18 patients (24%) were considered frail, and 11 (14%) were considered vulnerable. There was no significant difference in the frailty rate between directly admitted patients and transfer patients. In addition, no significant difference in in-hospital mortality was observed between patients with and without frailty (3.8% vs. 3.7%, respectively). However, there was a significant difference in frail patients’ 1-year mortality (6 out of 18 patients, 33%) compared to patients without frailty (2 out of 57 patients, 4%) and vulnerable patients (1 out of 11 patients, 9%). Logit-linked binary generalized estimating equations models controlling for age, number of rib fractures, ISS, and whether the patient was transferred, showed that each 1-point increase in the total frailty score was significantly associated with a 1.43 increase (95% confidence interval, 1.01–2.01; P=0.044) in the adjusted odds of mortality at 1 year postdischarge.
RESULTS
- Rib fractures, a common injury in trauma patients, present a conundrum for researchers. Rib fractures are often associated with other injuries, making analysis and broad treatment recommendations difficult. As this study shows, rib fractures can occur in any age group, and injury severity can greatly vary, with ISSs ranging from 1 to 75. We also found that the mechanisms of injury that led to rib fractures varied greatly between the different age groups. Furthermore, as age increased, low-risk mechanisms of injury, such as falls, comprised the overwhelming number of admissions. A recent analysis of the National Trauma Data Bank examined all patients with rib fractures in the United States from 2002 to 2006 and reported a mean age of 45.8 years and an overall mortality rate of 8% [17]. Our patient population was older than this cohort, with a median age of 57 years at the time of hospitalization, and had a lower in-hospital and 30-day mortality rate of 4.1%.
- We found few significant differences in outcomes between patients that presented directly to our trauma center and those who were transferred from another hospital. We did find that transfer patients had higher risk mechanisms of injury, a higher median ISS, and a higher likelihood of injuries associated with alcohol use. Our transfer population came from a large rural area that is served by many CAHs. It makes sense that transfer patients had a higher median ISS since patients with less severe injuries may be able to receive effective treatment from lower-level trauma centers. While no significant differences in in-hospital or 30-day postdischarge mortality rates were observed, we did find that patients transferred from other hospitals were more likely to experience unplanned ICU admission compared to directly admitted patients. While this study was not able to assess the causes for this disparity, it is possibly due to a lack of recognition of early decompensation or poor pain control or pulmonary care prior to transfer.
- Access to trauma care in rural areas is important, and a smooth system for transfer after the initial workup is necessary. In other studies of less developed trauma systems, transfer status was found to be associated with worse outcomes [18]. This study is likely biased due to the well-developed trauma system in our area. This study also highlights the importance of CAHs, as 82% of patients were initially evaluated at a critical access hospital. Without these hospitals, access to trauma care would be greatly limited. The majority of these CAHs were level III or IV designated trauma centers and all provide important care to patients who otherwise would not have close access to hospital care. Carr et al. [19] reported that 29.7 million people in the United States lacked access to a level I or II trauma center within 60 minutes via an ambulance or helicopter. Significant disparities exist in areas without this access, since they tend to be rural areas with a higher proportion of nonwhite residents and a higher uninsured population [19]. CAHs in these underserved areas can provide initial support and trauma stabilization for patients and, coupled with well-developed trauma systems, save lives.
- While current expert opinion and other low-evidence guidelines recommend ICU admission for all patients with rib fractures over the age of 65 years, it is unclear if this cutoff is ideal [11]. At our center, we do not currently have an age-based cutoff for ICU admission with rib fractures. The majority of our older patients are admitted to our trauma floor, which is staffed by well-trained trauma nurses and many advanced-practice providers who make frequent rounds. The entire trauma team is responsible for ensuring patients receive aggressive pulmonary hygiene treatment and quickly identifying any decompensation. We found that our rate of unplanned ICU visits was higher in patients younger than 65 years of age, further supporting that age is not the only risk factor. This finding is similar to many other studies that evaluated the outcomes of older patients with rib fractures, which raises questions about the necessity of ICU admission for all older patients with rib fractures [12,20]. It is likely that instead of a blanket recommendation for all patients of a certain age to be admitted to the ICU, identifying the patients at the highest risk of decompensation and poor outcomes is most important. As this study demonstrates, age is only a single, nonspecific factor when considering patient outcomes.
- Frailty and chronic comorbidities likely contribute significantly to worse outcomes in older patients with rib fractures. A higher number of comorbidities was associated with an increased mortality risk and was a similar predictor to age. In this study, we found that patients that were frail or vulnerable had similar outcomes in the hospital to other older patients except with significantly worse long-term outcomes. Identifying patients with frailty and chronic comorbidities that place them at higher risk may help prevent and treat early problems that lead to decompensation, identify modifiable risk factors that can improve their outcomes, guide discussions about the goals of care, and set patient and family expectations for recovery. Frailty is associated with increased mortality and morbidity and decreased independence after a traumatic injury [21]. Frailty rather than age may be the driver for the poor outcomes observed in older patient cohorts.
- This study is limited, however, since it was a single-institution retrospective study. In addition, we only collected frailty data for a small subset of patients. Further research is needed to better identify the risks posed by frailty concerning rib fracture outcomes, as well as to identify ways to modify the frailty level of patients. Furthermore, we did not collect data on other chest wall injuries associated with rib fractures, such as hemothorax, pneumothorax, flail chest, or displaced rib fractures, which likely affected the patients’ outcomes. This study does have several unique strengths, however, since our trauma center covers a unique population, serving a large, rural, and primarily elderly population. Therefore, this study could provide a predictive model for other trauma centers in the coming years as the aging population grows. This study raises several important questions that must be answered in the coming years. In particular, further research is needed to better identify which patients with rib fractures require transfer to trauma centers. In our well-developed trauma system, we did not identify any significant differences in the outcomes of transfer patients and directly admitted patients. We did identify that transfer patients tended to have more severe injuries since patients with less complex injuries likely received treatment at local hospitals. In addition, further research is needed to devise a detailed and accurate spectrum of risk factors that would prompt ICU admission of rib fracture patients. Age alone is insufficient, and clinical judgment should be used to ensure that limited resources such as ICU beds and nursing staff are not overutilized when they are not genuinely needed. Good bedside nursing and floor care can incorporate aggressive pulmonary hygiene treatment and enable the identification of patients who are not progressing as expected.
- Rib fractures can occur in any age group due to a vast array of injury mechanisms. The transfer of patients to trauma centers when appropriate and well-developed transfer plans between hospitals can ensure good outcomes for all patients, especially at trauma centers in rural areas. While older patients tend to be at risk for worse outcomes than younger patients, age is not as clear of a predictor of treatment outcomes as is commonly assumed. Frailty and many other complex interactions have a more substantial impact on which patients are at the highest risk.
DISCUSSION
-
Ethical statements
This study was reviewed, approved, and monitored throughout by the Institutional Review Board of Essentia Institute of Rural Health. Due to the retrospective nature of the study, informed consent was waived.
-
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
-
Funding
None.
-
Author contributions
Conceptualization: all authors; Data curation: KC, MH; Formal analysis: all authors; Methodology: KC, MH; Project administration: KC, MH; Visualization: KC, MH; Writing–original draft: all authors; Writing–review & editing: all authors.
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
-
Additional information
The data from this study was partially presented at the Minnesota Surgical Society Fall Conference on September 2019 in Saint Paul, MN, USA.
ARTICLE INFORMATION
Values are presented as number (%) or median (interquartile range). Patients with more than one unique hospitalization with rib fracture could be in both the direct admission and transfer groups. Analysis was performed using bivariate generalized estimating equations. Directly admitted patients were the comparison group.
ExpB, exponentiation of the B coefficient in binary logistic regression; CI, confidence interval; LOS, length of stay; ICU, intensive care unit; BiPAP, bilevel positive airway pressure; CPAP, continuous positive airway pressure.
Unadjusted ORs were calculated using univariate binary logistic regression, and the adjusted ORs (multivariate analysis) were calculated using all four variables controlling for sex (the adjusted OR for the female sex in the multivariate model was 0.82; 95% CI, 0.46–1.46).
OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval.
- 1. Ziegler DW, Agarwal NN. The morbidity and mortality of rib fractures. J Trauma 1994;37:975–9. ArticlePubMed
- 2. Sirmali M, Turut H, Topcu S, et al. A comprehensive analysis of traumatic rib fractures: morbidity, mortality and management. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2003;24:133–8. ArticlePubMed
- 3. Dunham CM, Hileman BM, Ransom KJ, Malik RJ. Trauma patient adverse outcomes are independently associated with rib cage fracture burden and severity of lung, head, and abdominal injuries. Int J Burns Trauma 2015;5:46–55. PubMedPMC
- 4. Flagel BT, Luchette FA, Reed RL, et al. Half-a-dozen ribs: the breakpoint for mortality. Surgery 2005;138:717–25. ArticlePubMed
- 5. Murphy CE 4th, Raja AS, Baumann BM, et al. Rib fracture diagnosis in the panscan era. Ann Emerg Med 2017;70:904–9. ArticlePubMed
- 6. Bulger EM, Arneson MA, Mock CN, Jurkovich GJ. Rib fractures in the elderly. J Trauma 2000;48:1040–7. ArticlePubMed
- 7. Bergeron E, Lavoie A, Clas D, et al. Elderly trauma patients with rib fractures are at greater risk of death and pneumonia. J Trauma 2003;54:478–85. ArticlePubMed
- 8. Shorr RM, Rodriguez A, Indeck MC, Crittenden MD, Hartunian S, Cowley RA. Blunt chest trauma in the elderly. J Trauma 1989;29:234–7. ArticlePubMed
- 9. Schmoekel N, Berguson J, Stassinopoulos J, Karamanos E, Patton J, Johnson JL. Rib fractures in the elderly: physiology trumps anatomy. Trauma Surg Acute Care Open 2019;4:e000257. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 10. Holcomb JB, McMullin NR, Kozar RA, Lygas MH, Moore FA. Morbidity from rib fractures increases after age 45. J Am Coll Surg 2003;196:549–55. ArticlePubMed
- 11. Tignanelli CJ, Rix A, Napolitano LM, Hemmila MR, Ma S, Kummerfeld E. Association between adherence to evidence-based practices for treatment of patients with traumatic rib fractures and mortality rates among US trauma centers. JAMA Netw Open 2020;3:e201316. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 12. Shi HH, Esquivel M, Staudenmayer KL, Spain DA. Effects of mechanism of injury and patient age on outcomes in geriatric rib fracture patients. Trauma Surg Acute Care Open 2017;2:e000074. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 13. Economic Research Service. Documentation: 2010 rural-urban commuting area (RUCA) codes [Internet]. Washington DC: US Department of Agriculture; 2019 [cited 2020 Dec 20]. Available from: https://www.ers.usda.gov/data-products/rural-urban-commuting-area-codes/documentation.
- 14. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). Critical access hospital [Internet]. Baltimore, MD: CMS; 2022 [cited 2022 Jan 3]. Available from: https://www.cms.gov/Outreach-and-Education/Medicare-Learning-Network-MLN/MLNProducts/Downloads/CritAccessHospfctsht.pdf.
- 15. American College of Surgeons (ACS). National Trauma Data Standard data dictionary 2021 admissions [Internet]. Chicago, IL: ACS; 2020 [cited 2020 Dec 21]. Available from: https://indd.adobe.com/view/d9ca99df-fda7-4991-ad99-a8cecf848965.
- 16. Rolfson DB, Majumdar SR, Tsuyuki RT, Tahir A, Rockwood K. Validity and reliability of the Edmonton Frail Scale. Age Ageing 2006;35:526–9. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 17. Whitson BA, McGonigal MD, Anderson CP, Dries DJ. Increasing numbers of rib fractures do not worsen outcome: an analysis of the National Trauma Data Bank. Am Surg 2013;79:140–50. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 18. Hill AD, Fowler RA, Nathens AB. Impact of interhospital transfer on outcomes for trauma patients: a systematic review. J Trauma 2011;71:1885–901. ArticlePubMed
- 19. Carr BG, Caplan JM, Pryor JP, Branas CC. A meta-analysis of prehospital care times for trauma. Prehosp Emerg Care 2006;10:198–206. ArticlePubMed
- 20. Barry R, Thompson E. Outcomes after rib fractures in geriatric blunt trauma patients. Am J Surg 2018;215:1020–3. ArticlePubMed
- 21. Poulton A, Shaw JF, Nguyen F, et al. The association of frailty with adverse outcomes after multisystem trauma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Anesth Analg 2020;130:1482–92. ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

 KST
KST

 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite